The first event that we editors attend each year usually is the annual WCBP (Well-Characterized Biopharmaceutical Products) conference hosted by CASSS, formerly the California Separations Science Society. Held in Washington, DC, each January, the meeting is prefaced by a day-long offering of two CMC Strategy Forums. The combined event brings together scientists and regulators from around the world to explore current issues in biopharmaceutical development from a chemistry, manufacturing, and controls (CMC) perspective. Presentations often include updates and progress reports on regulatory harmonization toward making and marketing life-saving therapies for a global patient population.
The best practices highlighted at those events tend to preview what will arise in other meetings throughout the year, so we watch this program closely for high-priority topics. For example, the industry has been buoyed by the rapid success of mRNA vaccines as well as established methods and comfort levels working with monoclo...
HTTPS://WWW.ISTOCKPHOTO.COM
Pharmaceutical companies and regulatory agencies strive to foster scientific excellence in drug development and evaluation so that members of the public can access the high-quality medicines that they need. Recent European Medicines Agency (EMA) approvals for COVID-19 vaccines highlight those organizational accomplishments and showcase the application of risk-based chemistry, manufacturing, and controls (CMC) flexibilities that are embedded within the European Union (EU) regulatory system.
Many of the CMC flexibilities outlined herein were established for PRIME (
priority medicine
), a scheme that the EMA launched to support and fast-track drug development. In April 2022, as the COVID-19 omicron variant spread throughout Europe, the EMA published guidance detailing a set of EU regulatory framework tools. Those tools are used for the completion of Module 3 in marketing-authorization applications (MAAs) of PRIME products that target unmet medical needs and are undergoing accelera...
For many life-science researchers at universities and other institutions, documenting and disseminating discoveries through publication is the natural culmination of their work. It is the process by which researchers, a group that includes principal investigators (PIs), postdoctoral researchers, and graduate students, advance their careers. It is a core piece of their continual efforts to secure funding for future work.
Most researchers are rewarded for the number and quality of their publications, which are judged, in part, by their impact factor (
1
). By publishing discoveries in respected, peer-reviewed journals, researchers build their reputations and credentials, smoothing the process of securing grants to fund additional research and discovery, leading to a cycle of success and job security. Although that research-to-funding ecosystem fuels important discoveries and groundbreaking innovations, a glaring gap often remains ignored: the protection of intellectual property (IP) rights. The emphasis on ...
HTTPS://STOCK.ADOBE.COM
Human medicinal product manufacturers face complexity and uncertainties regarding operational performance. Effective training management plays a major role in support and implementation of a pharmaceutical quality system. The minimum regulatory requirement is to employ adequately trained personnel with sufficient knowledge, skills, and experience. Software-based e-learning training methods are used widely across pharmaceutical companies. Achieving quality compliance depends significantly on several factors, from training preparation to assessments.
To comply with the current regulatory requirements, pharmaceutical companies need to implement learning management systems for training their employees — either e-learning or classroom (paper) based — as part of their overall quality systems. All such processes carry some residual risks and challenges during implementation. Based on regulatory agency inspection findings and industry expert perspectives, inherent risks in training process...

 +1
+1Failure to detect breaches in chromatography column performance can be disastrous during large-scale commercial manufacturing. Our company uses algorithm modeling for near–real-time monitoring of column packing quality and sensitive detection of column-integrity breaches. The approach enables us to mitigate risks early on, save cost and time, and thereby deliver consistent product quality and purity during manufacturing.
Here we discuss three case studies in which predictive algorithm modeling using moment analysis and direct transition analysis (DTA) helped us monitor column integrity and performance. We analyzed four performance indicators using production-scale chromatography data.
Preparative chromatography remains the method of choice to obtain high levels of purity during biologics manufacturing. However, the complexity of protein chemistry and upstream process variations complicates efforts to ensure consistent product quality during chromatographic purification. Effective monitoring of column perf...

 +4
+4WWW.ISTOCKPHOTO.COM
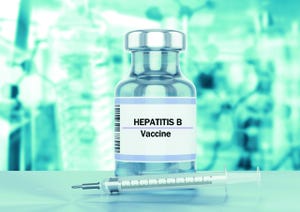
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), more than 350 million people worldwide are chronic carriers of hepatitis B virus (HBV) (
1
). Around 25% of carriers develop liver cirrhosis and/or carcinoma, making HBV responsible for the deaths of one million people annually (
1
).
The virus has a spherical shape with a lipoprotein coating mostly of HBV surface antigen (HBsAg) (
2
). Knowing that, drug developers have created recombinant HBV vaccines based on HBsAg synthesized in yeast or mammalian cells (
3, 4
). For such purposes, transformed cells are cultured in industrial-scale fermentors, after which expressed antigen is collected, purified, and formulated into spherical particles that expose the highly immunogenic “a” antigenic determinant region (
5
).
The Center for Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology (CIGB) in Havana, Cuba, produces HBsAg used in manufacture of recombinant vaccines against HBV (6). Because of the center’s efforts, Cuba is one of the few countries in the w...

 +6
+6Environmental monitoring (EM) remains an essential detection tool for cleanrooms within healthcare and pharmaceutical-manufacturing facilities. During monitoring, an agar growth medium is incubated at a specific temperature for a set time. There is no single approach to incubation. Researchers have performed several EM incubation studies, with results reflecting a diversity of practice. Typically, biomanufacturing sites either run selective monitoring sessions using single-incubation regimes with two different culture media, or they leverage a dual-incubation system using two temperature ranges with a single agar plate transferred between them. The latter strategy involves some compromise over what types of microorganisms can be recovered (
1
). But that concern is balanced by cost savings and avoidance of cross-contamination risks that can arise from doubling the number of needed interventions, such as into the aseptic core of grade A environments. With both approaches, the rationale is that higher tempe...
The growth of gene and cell therapies (CGTs) and specialty pharmaceuticals represents a radical shift in the treatment of rare diseases. By changing the parameters for care coordination, such innovations are improving patient outcomes and leading to a better quality of life. Treatments for rare diseases have been shown to provide more significant health benefits on average than can drugs that are formulated for more common conditions. Regrettably, over 95% of rare-disease patients in the United States lack a US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved treatment for their condition.
Specialty drugs treat rare and orphan diseases and complex chronic conditions. A high-touch disease state requires special handling, administration, distribution, storage, and/or monitoring. Treatment regimens can involve frequent patient care management or clinical monitoring of drugs. The drugs reach patients through a limited distribution network (LDN) and are expensive, which often adds a barrier to patient access.
Gene ...