Voices of Biotech
Podcast: MilliporeSigma says education vital to creating unbreakable chain for sustainability
MilliporeSigma discusses the importance of people, education, and the benefits of embracing discomfort to bolster sustainability efforts.

Protein A chromatography is still the preferred capture step in monoclonal antibody (MAb) production because of its high selectivity and robustness, although cation-exchange (CEX) or multimode chromatography techniques are claimed as alternatives. KANEKA KanCapA increases the value of protein A affinity chromatography for MAb production.
Kaneka’s unique combination of a proprietary-designed alkaline stable protein A ligand and a highly cross-linked cellulose base matrix meets customer requirements for improved performance, high binding capacity, alkaline and chemical stability for cleaning in place (CIP), mild acidic elution pH, limited nonspecific binding, and scalability with good pressure flow characteristics. KANEKA KanCapA is therefore a powerful tool for improving your MAb purification platform.
Dedicated Design of Protein Aligand
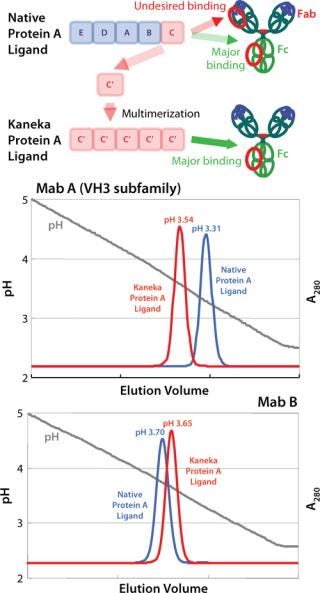
The elution profile of a Protein A column is a critical factor at industrial scale. For example, the VH3 subfamily of MAbs requires lower elution pH than other MAb types due to an additional protein A binding site in the Fab region. It is well-known that lower elution pH leads to higher aggregate formation. Kaneka eliminated Fab binding to the protein A ligand and narrowed the elution pH to mild acidic conditions for all MAb types.
Using computer-aided molecular calculation, three-dimensional (3D) structural model analysis of the C domain/Fab complex, and passive screening of genetically engineered ligands with several amino acid substitutions, Kaneka created a novel protein A ligand that makes it possible to select mild acidic conditions for elution. And Kaneka’s protein A ligand can be used under harsh alkaline conditions for CIP (see below).
Figure 1 shows the new ligand construction and improved elution profile for the VH3-encoded MAb. Elimination of binding to the Fab region makes it possible to elute all types of MAbs using mild acidic conditions (pH 3.5–3.8) and simplifies process development of a MAb purification platform.
Alkaline Stability
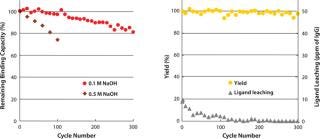
CIP with sodium hydroxide is a robust cleaning and sanitization step for chromatography resins. Kaneka’s new ligand has excellent alkaline stability and can withstand ≤300 cycles using 0.1M sodium hydroxide as a CIP solution for 15 minutes of contact time, with a limited loss of binding capacity (~20%). In addition, 0.5M sodium hydroxide can be used ≤100 cycles (Figure 2). Yields in elution pools are stable, and leaching of protein A ligand does not increase during cycle use. Because alkaline CIP can eliminate use of urea or guanidine-HCl, handling costs for dealing with such hazardous and expensive corrosive reagents are significantly reduced.
Highly Cross-Linked Cellulose for Easy Scale-Up to Production
A cellulose base matrix has nonspecific binding characteristcs superior to those of other matrices, polymers, or glass. Cellulose is biocompatible and has been used for many years in the plasmapheresis and dialysis fields. KANEKA KanCapA uses cellulose beads produced by a innovative highly cross-linking technology. This has allowed Kaneka to develop a resin that is easy to use, durable, and applicable to large-scale operations.
Figure 3 shows pressure and flow-rate characteristics, and Table 1 lists packing efficiencies of columns from 4.4-cm to 45-cm ID and 20-cm bed height. A 10% glycerol solution wasused to simulate viscous cell culture feed stock in a 45-cm ID column, and it showed reasonable pressure increase.
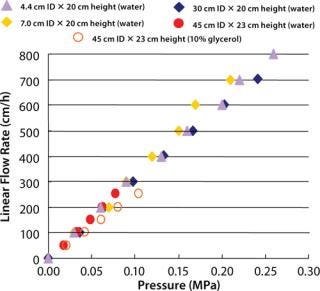
Table 1:
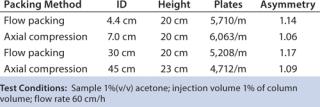
KANEKA KanCapA can be packed using flow or axial compression packing methods from pilot to large scale without special equipment and techniques. The columns show excellent pressure flow characteristics with good column performance.
High Performance in MAb Production
In selecting a chromatography resin, dynamic binding capacity (DBC) is an important parameter related to productivity and production cost. KANEKA KanCapA achieves high productivity at residence times of 4–6 minutes (Figure 4). Moreover, a steep elution peak is observed using small elution volumes with mild elution pH, and both low- and high-titer feed stocks can be treated using this KANEKA KanCapA (data not shown).

In conclusion, KANEKA KanCapA demonstrates an overall high performance in the MAb capture step, making it an indispensable tool for your MAb purification platform. As excellent performance has been acknowledged, several global pharmaceutical companies have already selected KANEKA KanCap A.
About the Author
Author Details
Koji Iritani ([email protected]) and Hideo Kitahashi are managers, and Takumi Sato and Keisuke Bando are marketers in the biochemical and medical business development division’s healthcare group of Kaneka Corporation, 2-3-18 Nakanoshima, Kita-ku Osaka 530-8288, Japan; www.fcd.kaneka.co.jp/biobusiness/kancapa.
You May Also Like