Niche Disease: Legionnaires’ Disease
by Cheryl Scott
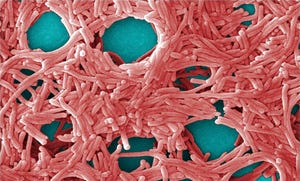
Colorized scanning electron micrograph (5,000×) by JH Carr depicts a large grouping of Legionella pneumophila bacteria. PUBLIC HEALTH IMAGE LIBRARY, CENTERS FOR DISEASE CONTROL (HTTP://PHIL.CDC.GOV)
Gram-negative, aerobic
Legionella pneumophila
bacteria were first identified as the cause of an outbreak of severe pneumonia at an American Legion Convention in a Philadelphia convention center in 1976. Since then (and probably long before), it has been responsible for occasional such outbreaks around the world. For example, an epidemic of the disease probably occurred in Minnesota in 1957. Such incidents are usually associated with poorly maintained artificial water systems (e.g., cooling towers and evaporative condensers, hot and cold water systems in public and private buildings, and whirlpool spas). The most common form of
L. pneumophila
transmission is through inhalation of aerosols related to contaminated water, aspiration of contaminated water, an...
KEMWELL BIOPHARMA (WWW.KEMWELLBIOPHARMA.COM)
Both small and large biopharmaceutical companies are increasingly pursuing the outsourcing of manufacturing and testing throughout the product lifecycle. The growing use of contract manufacturing organizations (CMOs) and contract testing organizations (CTOs) has led to increasing complexity within the biopharmaceutical industry as more third-party sites are leveraged to support global markets.
To address those issues, a CASSS Chemistry, Manufacturing, and Controls (CMC) Strategy Forum was held in Washington, DC, 27–28 July 2014. The title was “Effective
Management of Contract Organizations: Sponsors, Contract Organizations, Health Authorities and Patients — Keeping the Product Pipeline Moving, Compliant, and
Available.” The CMC Strategy Forum is a series of meetings that focus on emerging and relevant CMC issues throughout a product’s life cycle. The forums foster collaborative sharing of information among industry participants and regulatory agencies. Their go...
Medicalexpo
MERCK MILLIPORE (WWW.MERCKMILLIPORE.COM)
Single-use systems (SUS) consist of numerous plastic components derived from different suppliers. As such, they are prone to changes, including alterations in construction materials or modifications in manufacturing processes. Such changes may originate at the immediate supplier or farther back in the supply chain as a result of product improvements, process improvements, part discontinuation, or even business decisions such as manufacturing site relocation. Whether those changes are major or minor, managing their impact on biopharmaceutial processes and product quality often is a difficult undertaking in view of regulatory requirements.
The issue of change notifications for SUS is not new. Single-use plastic manufacturing equipment such as filters and bags has been used for decades. But until now, no industry- wide effort to streamline the process has been undertaken, and best practices have not been established. Given the rapid uptake of SUS, there is...
High costs and long timelines for biopharmaceutical development are cause for reflecting on how best to allocate resources from the earliest discovery stage through critical go–no-go junctures. With inputs ranging from science, engineering, and economics, the coined term developability becomes the synthesis of answers to such questions as
Attrition of therapeutic candidates during clinical development is the major factor in high development costs. Dollar and year figures vary too widely to quote any single source. And related statistics are based on averages, incorporating resources devoted to molecules that fail. Gaining control over the timing of failure through developability assessment becomes critical.
Developability assessment teams are multidisciplinary by necessity. They are charged
with evaluating potential drug candidates to allow pharmacologically effective new biological entities with favorable toxicity/immunogenicity and efficacy profiles to proceed through development. This presumably decrea...
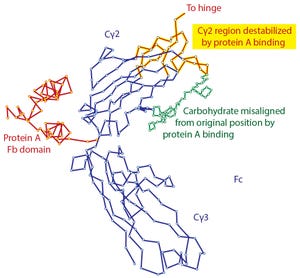
Figure 1: Denaturation of IgG by contact with protein A as shown by X-ray crystallography; modified from (
11
,
12
)
Affinity chromatography with protein A has become the foundation for purification of nearly every therapeutic IgG in commercial production. One of the features most responsible for its success has been its compelling simplicity. IgG binds. Contaminants do not. Load, wash, and elute pure IgG. In the real world, however, protein A does not elute pure IgG. It typically contains several hundred to a few thousand parts per million (ppm) contamination by host-cell proteins (HCPs) and other contaminants.
Numerous studies demonstrate why the biospecificity of protein A fails to deliver the purity it should be capable of. Contributing factors include phenomena such as nonspecific interactions between host contaminants and the base matrix of the chromatography media (
1
–
3
), nonspecific interactions between host contaminants and the protein A ligand (
3
–
5
), and nonspecific interactions between ...
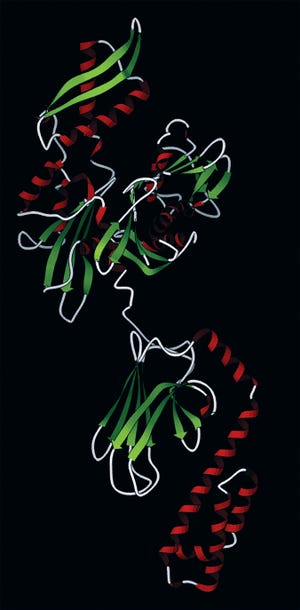
Hsp70 (pdb database 2KHO): Upper nucleotide-binding domain can bind to adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and adenoside diphosphate (ADP), lower is a subtrate-binding domain. (WWW.WIKICOMMONS.COM)
Recombinant therapeutic proteins are commonly produced by cell lines such as Chinese hamster ovary (CHO), human embryonic kidney (HEK) 293, murine myeloma (NS0), and
Escherichia coli
bacterial cells. Host-cell proteins (HCPs) are indigenous proteins produced by those expression hosts and considered to be process-related impurities generated from the cell culture process (
1
). HCPs are potentially harmful and immunogenic to patients, and they can compromise the stability of protein drugs (
2
–
4
). For those reasons, HCPs must be consistently removed or reduced to acceptable levels during downstream processes to ensure patient safety. Regulatory agencies require manufacturers to adequately control HCP levels, demonstrate of HCP clearance throughout a product manufacturing process, and monitor residual HCP levels in ...
Trainees attend a QC/Analytical course at BTEC in February, 2014. BIOMANUFACTURING TRAINING AND EDUCATION CENTER
Biopharmaceutical manufacturing involves complex process steps. Exacting production conditions are typically required to maximize the yield, purity, and quality of biological products. In recent years, process analytical technology (PAT) has been increasingly used to monitor key process and performance parameters in real time. That has enabled better control of production conditions. An important parameter required to achieve consistent results in many bioprocessing steps is solute concentration in process fluids.
The Critical Need for Concentration Measurement
Many biopharmaceutical manufacturing process steps require measuring the concentration of solutes in solutions. For upstream processes, concentration of components in feeds and in bioreactors is critical to cell metabolism and growth as well as to ensuring reproducible operations.
In downstream processes, numerous solutions (including bu...
Blow–fill–seal (BFS) technology has been recognized by the industry as an advanced aseptic solution (
1
–
3
). Catalent Pharma Solutions has been commercially supplying sterile BFS products to the pharmaceutical industry for decades, primarily in the respiratory and topical ophthalmic markets. Such product formulations range from simple solutions to emulsions with drug substances from classical small molecules to large complex proteins such as biologics. The company also has optimized BFS processes and its Advasept plastic container system for the manufacture of sterile injectable products.
The Advasept container system provides significant advantages over traditional, commercial, glass container systems for the parenteral/injectable market space. Benefits include reduced container breakage and an absence of glass delamination (
4
). The automated aseptic filling design of BFS advanced aseptic technology drastically reduces the risks associated with traditional aseptic manufacturing. BFS forms, fills, and...
In the past year, CPhI Worldwide (a division of UBM EMEA) has released reports on both the Indian and Chinese pharmaceutical markets, findings of which were presented at CPhI India in Mumbai in early December 2014 and shortly after CPhI China in August 2015.
India Looking Outward to Innovate
The Indian report,
CPhI India Pharmaceuticals 2015: Industry Explorations
, was developed by CPhI in partnership with Global Business Reports (GBR) to provide a comprehensive analysis of the country’s pharmaceutical market. Overall, Indian companies are confident about near- and medium-term growth potential, as outsourcing and exports push ahead with growth at a double- digit pace. Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) that have traditionally relied on their domestic market are expanding and emerging as multinational corporations (MNCs) based on export-led growth strategies.
One key region to emerge for Indian exports is Japan, a country that is now opening its doors to overseas penetration. Another key area will...
with Thomas Flouquet (Novasep)
The first simulation and optimization software for chromatography process development in biopharmaceutical purification, the BioSC Predict program from Novasep received an 2015 Achema award for Pharmaceutical Engineering. Driven by user objectives, it can define practical constraints and desired strategies. Optimization algorithms provide the most adapted operational conditions for a BioSC system. In a webcast on 17 September 2015, Novasep’s Thomas Flouquet demonstrated the software’s functionality and customizability. He presented optimized recipes taking into account parameters such as process type, feed titer, load velocity, number of columns, and resin bed height. Below is a summary of his presentation. You can find more detail and the full slide presentation online.
Flouquet’s Presentation
BioSC Predict simulation software optimizes the protein capture step with affinity, ion-exchange, and hydrophobic solvents. It maximizes solvent use to achieve a user’s objectives r...
with Dr. James Brooks (BD Biosciences)
Improvements in cell culture media and supplementation have enabled significant advancements in bioproduction titers. But optimization to meet the specific needs of individual production cell lines is key to achieving desired production and protein quality, especially for biosimilars. Not only is it desirable to achieve cost-effective levels of production, but quality characteristics also are essential — and for biosimilars must closely resemble those of the originator molecules.
Fully chemically defined (CD) media formulations are desirable for their presumed consistency and risk reduction, such formulations may or may not meet production or quality requirements. Depending on nutritional and culture requirements of a cell line and process, both CD supplements and protein hydrolysates have been shown to provide necessary supplementation for desired production and protein quality. In a webinar on 2 September 2015, Dr. James Brooks (R&D manager at BD) illustrated how h...
PREPRINT
October 2015 issue
Blow–fill–seal (BFS) technology has been recognized by the industry as an advanced aseptic solution (
1–3
). Catalent Pharma Solutions has been commercially supplying sterile BFS products to the pharmaceutical industry for decades, primarily in the respiratory and topical ophthalmic markets. Such product formulations range from simple solutions to emulsions with drug substances from classical small molecules to large complex proteins such as biologics. The company also has optimized BFS processes and its Advasept plastic container system for the manufacture of sterile injectable products.
The Advasept container system provides significant advantages over traditional, commercial, glass container systems for the parenteral/injectable market space. Benefits include reduced container breakage and an absence of glass delamination (
4
). The automated aseptic filling design of BFS advanced aseptic technology drastically reduces the risks associated with traditional aseptic manufactu...