October 2019 Featured Report
Photo 1: TideXCell bioreactor platform from Esco Aster (Photo courtesy of Esco Aster)
This year’s BioProcess International Conference and Exhibition, held 9–12 September 2019, hosted nearly 200 exhibitors showcasing technical innovations for the biopharmaceutical industry. This year’s conference sessions also included daily technical workshops detailing supplier solutions and technologies. Below are some notable technologies featured that demonstrate the industry’s dedication to finding new ways to help manufacturers shorten time to market. Most systems offer the benefits of single use, integration, process control, economies of scale, automation, and closed-system processing.
Upstream Production
The exhibit floor had only a few booths from bioreactor suppliers, and most were familiar systems in single-use design and pilot and laboratory scales. Newer systems offered improved integration with software platforms and an increase in sensor monitoring. And there was a notable increase from last year in the nu...
Bioprocess manufacturers continue to seek technologies for increasing productivity and shortening timelines from discovery to commercialization. Innovations such as high-throughput systems, automated platforms, and the latest clarification systems all have made processes efficient and robust. And with the increasing adoption of quality by design (QbD) principles, including the use of process analytical technologies (PAT), biomanufacturers are mitigating the risks of errors in their operations better than ever before. A critical part of mitigating risk is gathering meaningful process data and then relating those data points to information about product quality. Smart facility management starts with the implementation of solutions that can relate those data to decision makers quickly — ideally in real time — as part of one overall network.
To gain perspective on modern technologies and design approaches in bioprocess facilities, I spoke with Matt Roesch, senior director of life sciences at JLL Life Sciences...
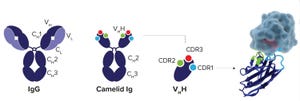
Figure 1: Regular IgG antibody compared with a Camelid single domain Ig antibody and VHH antibody fragment; the image on the far right shows VHH bound to its target protein.
The rapid and cost-effective production of conventional monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) for clinical trials and commercial supply has contributed toward their wide adoption. Production processes have become more efficient because common purification processes are being used across structurally similar MAbs during key steps of process development and manufacturing. Such successful platform approaches can remove unwanted impurities and are stable across processing conditions, irrespective of the MAb being purified. In addition, they are readily available at the required volume to support large-scale current good manufacturing practice (CGMP) production and can be validated easily. Platform approaches also minimize both the duration and number of steps in downstream processing operations, which contributes significantly to maximizing effici...
Figure 1: 5F9 (magrolimab) enables macrophages to phagocytize cancer cells by blocking the binding of the “don’t eat me” signal CD47 to its receptor SIRPα (
1
)
Forty Seven is a company developing novel therapies based on anti-CD47 and other immuno-oncologies. CD47 is called the “don’t eat me” signal that cancer cells give out to escape elimination by the body’s immune system. Qinghai Zhao, vice president of technical development and manufacturing, is one of the scientists working on the company’s magrolimab (5F9) monoclonal antibody that is designed to block the binding of the CD47 signal to the cell receptor SIRP-α while boosting the “eat me” signal that enables a patient’s own immune system to destroy the cancer cells (Figure 1).
At the 2019 BPI West conference in Santa Clara, CA, Zhao’s presentation focused on the importance of speed to investigational new drug (IND) application and the company’s process for selecting a platform and contract development and manufacturing organization (CDMO) for its ma...