WWW.LIFETOUCH.COM
Included with this issue is our first of two supplements this year focused on cell therapies. It has been fascinating to watch this journey toward maturation of advanced therapeutics. Some early assumptions that commonalities with protein production would resolve manufacturing problems are being tempered now that we know more about the unique demands of cell and gene therapy development. Still, the future looks brighter for these new modalities.
As Invetech’s Richard Grant (global VP, cell therapy) noted in his plenary address at the January Cell and Gene Therapy World conference in Washington, DC, advanced therapies are poised to revolutionize healthcare by 2025. The past year has seen progress toward removing three main obstacles to commercial success: solving technical challenges, driving down treatment costs, and aligning global regulatory approaches.
One challenge emphasized in this month’s supplement is reduction of manual intervention. It is clear now that scalable commercial solu...
WWW.GRAPHICSTOCK.COM
Preventing Vaccine Shortages
Few people worry about vaccine supply until a shortage occurs. New research from Duke University’s Fuqua School of Business focuses on market tensions that can keep vaccine manufacturers out of the business and price points needed to entice them in.
“The government doesn’t want to overpay,” says professor David Ridley, “but there’s a tension between responsible use of government funds and giving manufacturers sufficient incentives to get into vaccine manufacturing — and stay in.” Together with colleagues Xiaoshu Bei and Eli Liebman, he found that over the past decade, every 10% increase in vaccine prices corresponded with a 1% lower shortage probability
“Many people forego vaccines and jeopardize herd immunity,” Ridley explains, “putting at risk the health of people with compromised immune systems. That’s the demand side. But what about supply? How do we encourage suppliers to be in the business?”
Some children visit a doctor only once per year, so if a va...
ASME BPE standard-based parts from Nordson Medical NORDSON MEDICAL (WWW.SCVSERIES.COM)
With the escalating use of single-use technology in bioprocessing, suppliers have had to rapidly develop disposable components such as fittings, tubing, pumps, sensors, and flexible containers for bioprocessing. Single-use technology is growing so fast that the organizations tasked with guiding its growth are having difficulty keeping up. Contributing to this problem are factors such as company needs, regulatory requirements, market pressures, and costs.
That growth has posed considerable concerns for the bioprocessing industry about the presence of organic and inorganic particles within formulations, leachables, the hygienic integrity of connector unions, and control of single-use system component changes. As single-use technology advances, many bioprocessing experts realize that these areas require improvement, especially in detection and control of particles. The industry understands the potential expense and danger ...
WWW.GRAPHICSTOCK.COM REPRINT WITH PERMISSION
Drug development is a complex process that is associated with high drug-candidate attrition rates, long development times, and high costs (
1
,
2
). Drug development costs have increased over the past two decades, with current average development cost of about US$2.6 billion, of which $1.4 billion is the direct cost (
1
,
2
). On average, drug development takes at least 10 years to market authorization (
2
). Biopharmaceutical companies often follow a strategy of developing drugs for multiple clinical indications and biological targets simultaneously to increase probability of their drugs’ regulatory approval. Because multiple drugs can be commercialized for the same indication by different biopharmaceutical companies, time of exclusive market share is decreasing (
3
), and late-entrant drugs are sometimes unable to differentiate from existing commercial drugs. Contrarily, late-entrant drugs can take significant market share from established competitor drugs.
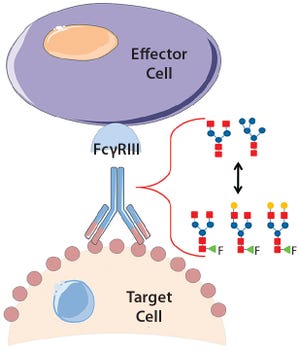
Product quality attributes are critical for the functionality and manufacturability of therapeutic antibodies. They can be significantly influenced by a number of production process parameters, such as cell culture media. The composition of growth and feed media can influence antibody glycosylation, including the concentration of ammonia, glutamine, glucose, and metal ions (
1
,
2
). Thus, it is critical during media development and optimization to monitor and consider a culture medium’s impact on glycosylation. For therapeutic antibodies whose mechanism of action includes antibody-dependent, cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC), it is particularly important to measure N-glycan fucosylation at Asn 297 in the Fc domain, which is well known to influence ADCC activity strongly (
3
,
4
).
In ADCC, an antibody first binds to a cell-surface target antigen, then recruits immune effector cells that lyse the target cell. A decrease in fucosylation at Asn 297 has been shown to increase the antibodies’ binding affini...
WWW.PHOTOS.COM
Monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) are at the focal point of biologics development. Many of the best-selling drugs are therapeutic MAbs or related proteins (
1
–
2
). The combined world-wide sales from MAbs will be nearly US$125 billion by 2020 (
3
). About 50 MAb products treating a range of diseases have been approved in the United States or Europe. With the large number of MAbs progressing through discovery, biomanufacturers need to accelerate process development and move projects rapidly into clinical manufacturing (
4
–
5
). Formulation development, an important aspect of product development, is often on the critical path to successful clinical manufacturing and stability studies, which are essential to investigational new drug (IND) filings. Discussions on leveraging platform processes to shorten process development timelines and save resources often focus primarily on upstream and downstream operations (
6
–
7
). Here we describe a rapid platform strategy for formulation development succes...
REPLIGEN CORPORATION (WWW.REPLIGEN.SE)
Time to market, resource requirements, cost, and flexibility are key considerations in designing purification processes suitable for manufacturing biopharmaceutical products. Over the past decade, many advances have been achieved in disposable processing systems that have allowed for increased processing at a lower cost. That is in part attributable to reductions in necessary resources, changeover costs, and cleaning-validation requirements.
Large-scale, prepacked chromatography columns have recently become available for clinical and commercial manufacturing, and they represent a growing trend in the industry. Prepacked large-scale columns could meet the needs of manufacturing with single-use technologies and may have many benefits. First, quality groups may consider such columns as consumables, eliminating the need for equipment capital and qualification, asset traceability, calibration, and routine maintenance. Second, companies also see reductions in column-packin...
WWW.PHOTOS.COM
About 60% of all drug targets are membrane proteins. So understanding their structure and function as well as their interactions with drug candidates is critical to discovery and development of new therapeutic agents. Solubilization of these proteins is an essential precursor to in vitro studies of receptor function, structure, and activity. Purification and crystallization are important aspects. However, solubilization is complicated by the hydrophobic nature of a protein’s membrane-spanning part. Surfactant micelles and other stabilizing systems thus are used to achieve successful solubilization of membrane proteins. That use in turn necissitates a detailed characterization of protein–detergent complexes (PDCs).
Here we look at the application of tetradetector size-exclusion chromatography (SEC) for analysis of membrane proteins, particularly PDCs. A key goal of this work is to identify pure, homogeneous, stable PDCs with minimal excess detergent micelles. Such results provide a good star...
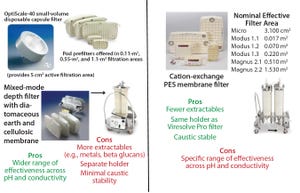
Figure 4: Description of Viresolve Prefilter (left) and Viresolve Pro Shield (right) adsorptive prefilters
Size-exclusion–based parvovirus filtration is an important step toward drug product safety in biopharmaceutical production. However, once a virus filter is in place, and the required virus safety is ensured, less attention typically is paid to its optimization within the process. That might seem odd given that virus filtration can be one of the more expensive downstream processing steps ($/g protein processed). Most likely, the lack of attention can be attributed to aggressive timelines, limited process development resources, and the virus filter’s inability to separate drug-product intermediates from host-cell protein and DNA impurities. Most biopharmaceutical process development resources are dedicated to the primary goal of achieving the required drug-product purity. For sound reasons, most of the process-optimization effort goes into critical chromatographic purification unit operations. However,...
Adding to the complexity of drug-product labeling, companies face a broad range of evolving requirements. Those include regional, language, customer, and regulatory requirements that must be met quickly and efficiently to prevent supply-chain disruption. Companies that cannot meet those requirements can end up with fines, dissatisfied customers, and loss of business. Enterprise labeling solutions allow drug makers to deal with variability in labeling by providing label formatting that supports myriad different label combinations with a minimum number of label designs.
Major Drivers Causing Labeling Variability
A number of issues can lead to variability in labeling, but the primary drivers are customer variability and regulatory requirements. No standard label works for every situation. Customers are becoming more demanding about the labels that appear on goods and products that they receive, distribute, and sell. The same standard product might have a product label that varies greatly based on the unique ...