November-December 2023
As I look forward to retirement and revisit 35 years in publishing, I marvel at all the adventures that a graduate degree in comparative literature can lead to. I’d always dabbled in biology, but for some years, literature, languages, and teaching won out. By the late 1980s, leaving a dissertation unfinished didn’t help me compete for full-time community college teaching gigs. Carpentry and school-bus driving were okay for a while, and playing baroque recorder music garnered extra grocery money, but none of those offered a good insurance plan.
On 8/8/88, I began as a proofreader at what was then Aster Publishing in Eugene, OR. Ed Aster was a local character with a talent for launching niche publications, many of which still exist today:
Pharmaceutical Technology, BioPharm, Spectroscopy, LC-GC,
and
Applied Clinical Trials
, to name a few. Using typewriters, outside typesetters, waxed pasteboards, and printers’ bluelines, I learned about old-style publishing and magazine editing. Soon I joined the staff ...
HTTPS://ADOBESTOCK.COM
Our world provides us with abundant data at every moment of every day that we constantly analyze to make decisions. What is most important in a business/laboratory context is that the data we receive be attributable, accurate, legible, permanent, contemporaneous, and original.
A company’s pharmaceutical quality system (PQS) plays a vital role in analyzing data integrity. As explained in ISO/IEC 2382:2015,
data
describe formalized representations of information suitable for communication, interpretation, or processing (
1
). According to the same ISO standard,
data integrity
refers to the preservation of accuracy and consistency regardless of changes made. Pharmaceutical companies heavily rely on data in their business operations. From drug development and preclinical research to clinical trials, manufacturing, and creation of a registration dossier, data sets play a crucial role in ensuring the quality, efficacy, and safety of medicines as well as building brand trust.
A signifi...
FLICKR.COM
The Personalized Medicine Coalition met in Washington, DC, in May 2023 to commemorate the 20th anniversary of the Human Genome Project’s completion. Eric Green, director of the National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI), has been a key contributor to the fields of genomics and personalized medicine for more than three decades. According to Lincoln Nadauld, cofounder and chief executive officer (CEO) of Culmination Bio, Green’s work has “included significant involvement in the Human Genome Project, during which he and his lab pioneered novel approaches for mapping and sequencing the human genome.” Green addressed constituents at the Personalized Medicine Coalition’s 15th Annual State of Personalized Medicine Luncheon to discuss medical advancements bolstered by the success of the genome project. Below, we present a summary of Green’s insights into human genomics and the future of medicine.
Green’s Presentation
Serving as one of 27 organizations that make up the US National Institutes of He...
HTTPS://WWW.ISTOCKPHOTO.COM
In the United States, a
rare disease
is defined as a condition that affects fewer than 200,000 people nationwide. The World Health Organization defines a
rare disease
as a disorder that affects fewer than 65 per 100,000 people (
1
). In the European Union, the definition narrows to five in 10,000 people. Ten percent of the global population is affected by at least one of the >10,000 identified rare diseases — which accounts for about
30 million people in the United States (
2
). Although the causes of most rare diseases are unknown, many such conditions are traced to mutations in a single gene. In fact, 80% of rare diseases have a genetic origin (
1
). The average time for diagnosis is four to five years. Many patients remain undiagnosed and receive only symptomatic treatment.
Orphan drugs
— medications used to treat rare diseases — offer several potential advantages, including shorter development timelines, reduced research and development costs, and limited generic compe...
Photo 1:
Microfluidic device as an option for automated high-throughput HCP analytics in early bioprocess development (
HTTPS://WWW.GYROSPROTEINTECHNOLOGIES.COM/ IMMUNOASSAYS/GYROLAB-TECHNOLOGY
)
Biopharmaceutical drugs are produced by a number of expression host systems, mainly mammalian (e.g., Chinese hamster ovary, CHO) and microbial (e.g.,
Escherichia coli
) cells. The goal of subsequent purification steps is production of a pure drug substance, which is essentially free of product variants and process-related impurities such as host cell proteins (HCPs) and nucleic acids. Depending on the process, HCPs can represent the total proteome of a host cell line and accordingly are highly diverse in size, charge, hydrophobicity, and function (e.g., enzymatic reactions).
Immunogenic HCPs can pose a potential risk for patients. Moreover, many HCPs can present a danger to a biotherapeutic product by facilitating its degradation or modification of the drug substance itself or its formulation (
1
). Therefore, ...
HTTPS://WWW.ISTOCKPHOTO.COM
As defined in ICH Q6A, a
specification
is a list of tests, references to analytical procedures, and appropriate acceptance criteria that take the form of numerical limits, ranges, or other criteria for the tests described (
1
). They establish the set of criteria to which a new drug substance or product should conform to be considered acceptable for its intended use.
Ideally, specifications are established based on demonstration of quality attribute levels that make drugs safe and efficacious during toxicology and clinical studies. At that point in development, however, analytical and process variability may not be reflected fully by the few drug lots used for such studies. Along with test data from toxicology and clinical studies, ICH Q6A cites relevant development data, pharmacopeial standards, and results from accelerated and long-term stability studies, as justification of specifications. Additionally, the guideline states that companies should take a reasonable range of ...
HTTPS://ISTOCK.PHOTOS.COM
Upstream process scientists and engineers actively monitor bioreactor metabolite levels during cell culture using off-line blood-gas analyzers (BGAs) and related instrumentation. But such tools introduce inherent variability into metabolite measurements. The magnitude of that variability depends on the measurement range.
Mammalian cells are sensitive to concentrations of one such metabolite: dissolved CO
2
. In cell cultures, CO
2
levels often are reported as partial pressure (pCO
2
) in millimeters of mercury (mmHg). Available literature frequently reports that elevated pCO
2
concentrations have adverse impacts on cell health, causing changes in cell metabolism, decreases in cell productivity, and altered glycosylation profiles in expressed therapeutic proteins (
1–3
). Thus, bioreactor CO
2
concentration often is designated as a critical process parameter (CPP) or in-process control (IPC) parameter with action limits of ~50–150 mmHg (typically <120–150 mmHg) to prevent the a...
As a direct result of the COVID-19 pandemic, mRNA-based therapeutics have made significant clinical and commercial progress. With many such therapeutics filling up the clinical pipeline for a growing number of indications, the biopharmaceutical industry is investigating efficient and scalable manufacturing techniques. For example, Thermo Fisher Scientific has developed a novel affinity chromatography resin with a poly(styrene-
co
-divinylbenzene) backbone and with throughpores to isolate and purify mRNA at various scales. Because the POROS Oligo dT(25) affinity resin binds mRNA through a simple adenine–thymine base-pairing mechanism, it can serve as a purification platform for all mRNA molecules containing a poly-A tail.
In this article, a Thermo Fisher scientist describes the advantages of affinity capture for mRNA therapeutics, then explores considerations for optimizing capture, including the influences of product size on precipitation point, resin dynamic binding capacity (DBC), and process elution co...
Detection and quantitation of process-related impurities are important to quality control in biopharmaceutical manufacturing. Process-related impurities can have a significant impact on pharmaceutical product quality, safety, and efficacy. Such impurities can be generated during a biomanufacturing process and come from product degradation, starting materials and reagents, by-products, storage conditions, and contamination. Without proper detection and quantification, process-related impurities can cause adverse effects in patients.
Guidelines from the International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH) make quality by design (QbD) an essential requirement during pharmaceutical development. The ICH Q8–Q10 documents outline a systematic approach to pharmaceutical development, emphasizing the crucial importance of understanding product and process parameters to ensure product quality (
1–3
). Below, I highlight key challenges in the detection and quantita...
Sponsored Content
As a contract development and manufacturing organization (CDMO), Aton Biotech provides a comprehensive set of services to clients developing biological drugs. Those services range from cell line development to clinical development and end-to-end commercial manufacturing.
A Long History
Aton emerged from a biopharmaceutical company called Henlius that was established in Shanghai, China, nearly 13 years ago. Today, Henlius has five products on the market including rituximab, trastuzumab, and adalimumab. From the beginning, company leadership decided to build internal manufacturing capacity to strike a balance between quality and efficiency.
In 2022, a team of experts spun out from Henlius to form Aton Biotech, which is now a separate legal entity. Aton fully leverages profound experience derived from Henlius in providing end-to-end services to other biopharmaceutical companies. We felt confident that we not only could replicate the success that Henlius has experienced, but also would establish a CDMO that s...
byMin Park
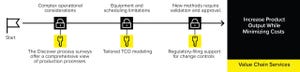
The biopharmaceutical industry is facing continued pressures to bring high-quality drugs to the market quickly while limiting costs and meeting challenging sustainability targets. However, companies might lack the expertise, resources, and time required to establish, optimize, and scale up tailored, efficient processes that meet market demands.
Process consultancy services and preengineered solutions are excellent resources that bring in new perspectives and expertise, regardless of your specific end goals. Here, we outline four key objectives, the challenges associated with meeting them, and a suitable service for each objective to help meet your needs.
Objective #1: Increase Output While Minimizing Costs
With the “patent cliff” approaching, biopharmaceutical companies already in commercial manufacturing must cope with increasing market pressure from biosimilar competitors. Therefore, maximizing process efficiency is critical. That includes increasing batch numbers and production yields while reducing ma...
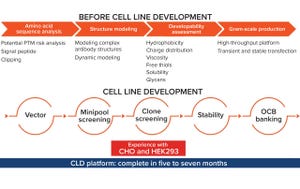
Traditional cell line development to support bioprocessing often has relied on a “one-size-fits-all” vector, which can lead to suboptimal expression levels in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cell cultures. Scott Estes (head of cell line development at Asimov) and his team have brought a rational approach to how cells are engineered. The CHO Edge system integrates knowledge from experts in cell line engineering, synthetic biology, software design, machine learning, and omics-driven modeling of metabolism and gene expression.
Estes’s Presentation
Estes explained that the CHO Edge platform engine is based upon Asimov’s robust CHO-K1 glutamine synthetase (GS) knock-out line. Asimov adapted CHO-K1 host cells from the European Collection of Authenticated Cell Cultures (ECACC) and used them to create glutamine auxotrophs. After genotypic and the phenotypic levels were characterized, a cell line was sent to Charles River Laboratories for creation of a master cell bank and safety, sterility, and identity testing. Asim...
Regulatory agencies require biopharmaceutical developers to demonstrate effective viral clearance during downstream processing. Historically, companies have outsourced clearance-validation studies to contract research organizations (CROs) that are equipped to spike samples with live pathogens, such as xenotropic murine leukemia virus–related virus (XMuLV). But as David Cetlin (senior director of MockV products from Cygnus Technologies) pointed out in a September 2023 “Ask the Expert” webinar, that strategy is cost- and time-intensive. Thus, developers often postpone viral-clearance assessment until late in process development, when it is disadvantageous to identify needed changes. Cetlin explained how MockV kits with retrovirus-like particles (RVLPs) enable developers to generate viral-clearance data quickly and economically in their own biosafety-level–1 (BSL-1) laboratories. He also highlighted how recent changes to the ICH Q5A guidance may allow for application of RVLPs during viral-clearance validatio...
Delivering safe and effective therapies starts in facilities that are built and maintained with safety and compliance in mind. US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and European Commission (EC) regulations often are presented as broad guidelines that describe what manufacturers need to account for, but they are not always prescriptive because facilities have unique needs. In a September “Ask the Expert” webinar, Gerardo Gomez and Patrick Nieuwenhuizen of PharmaLex Solutions demystified the guidelines that bioprocessing companies should follow.
The Presentation
Gomez explained that facility design is a crucial step to ensuring compliance with FDA regulations. In accordance with FDA 21 CFR Part 211, building size, construction, and location all influence a company’s ability to clean, maintain and properly operate a facility (
1
). Each operation must be performed within predefined areas of adequate size to prevent mixing up and contaminating drug components, product containers, closures, and labels. Many fa...
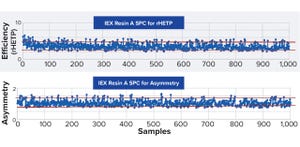
Figure 1:
More than 1,000 data points demonstrate reproducible ion-exchange (IEX) resin packing while maintaining robust quality across eight years. Red lines denote upper and lower confidence limits, with 99% <3σ and 96% <2σ for efficiency, and 98% <2σ and 99% <3σ for asymmetry. rHETP = reduced height equivalent of theoretical plate.
In September 2023, Adam Nelson (chromatography product manager at Repligen Corporation) led an Ask the Expert webinar on applying statistical process-control (SPC) analysis to assess performance consistency for prepacked chromatography columns.
Nelson’s Presentation
OPUS prepacked chromatography columns come in a range of formats, from small-scale RoboColumn, MiniChrom, and ValiChrom columns for process development and process validation to large scale columns for clinical and commercial manufacturing. Customers specify the diameter, bed height, and resin to be packed inside their columns. As the product line has expanded from its initial launch in 2012, Repligen has gather...
Subscribe to receive our monthly print or digital publication
Join our 70,000+ readers. And yes, it's completely free.









.png?width=300&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)